Benchmarking Denoising Algorithms with Real Photographs
2021/9/15
来源:CVPR17
resource:github上备份的包括ipad标注的pdf版本。
作者是TU Darmstadt的Tobias Plotz和Stefan Roth,挺有价值,但是难懂。
Summary:知识密度很高的一篇文献,从里面接触了图像噪声的一些信息。本篇文献提供了一个新的Raw Real Image数据集(方法是将低ISO长曝光时间的图片当做准纯净图像,对应高ISO短曝光时间的图片当做噪声图像,保证二者乘积相同),并且认为之前的数据集获取纯净图像的方式有问题,提出了制作纯净图像的pipeline,包括Linear intensity changes(对齐感光度、曝光时间误差)、Lucas-Kanade Approach(Spatial misalignment)、Low-frequency residual correction(避免光照随时间变化)。后面有对pipeline有效性的证明实验,但是没有相关背景知识,没看懂,暂时也不需要懂。
Key words:
- 噪声原理
- 真实图像(raw)去噪benchmark
Rating: 4.0/5.0 还是比较有价值的,感觉对理解噪声很有帮助。
Comprehension: 2.0/5.0 但是后面方案有效性的证明缺少太多preliminary所以没有看懂(目前对我而言不重要)。
Abstract
- 将不同ISO/Exposure Time(两者乘积相同)的图像对作为纯净-含噪图片对。
- 进一步引入了处理"纯净图像"的pipeline,用一种线性强度变换(linear intensity transform校正了因为相机震动等因素产生的图像像素不匹配、exposure param不准确的问题,并去除了光照强度变化变化的影响(附原文:
We capture pairs of images with different ISO values and appropriately adjusted exposure times, where the nearly
noise-free low-ISO image serves as reference. To derive the ground truth, careful post-processing is needed.
We correct spatial misalignment, cope with inaccuracies in the exposure parameters through a linear intensity
transform based on a novel heteroscedastic Tobit regression model, and remove residual low-frequency bias that
stems, e.g., from minor illumination changes.
1. Introduction
- 噪声广泛存在于图像系统中,低光场景尤甚。
- 采集含噪图片很简单,但是纯净图像的采集很困难(制作数据集的难点)。
- 噪声合成过程中的一些细节,比如含噪值是否被round成整数都会对结果产生很大影响。
- 第二段的总结很好,pipeline包括:
- heteroscedastic Tobit regression model generalizing以去除由于analog gain of the sensor(ISO)与exposure time都不准确(多少有点误差,每次)产生的图片之间的线性依赖关系
- the model faithfully accounts for clipping as well as signal-dependent noise
- 光照的微小变化会导致低频偏差,通过在变换域(这里noise process是零均值的)中高通滤波含噪图片与参考图片之间的残差以去除
- 处理移动物体
- 用Lucas-Kanade subpixel alignment解决了相机震动引起的pixel misalignment
- 商业相机中的噪声强度要显著低于学术假设的噪声水平
- 去噪要在raw domain里去,不要在sRGB里去!
2. Related Work
有对噪声原理的精彩解释。
- CCD/CMOS图像中的噪声源包括:
- short nosie,光子撞击sensor的随机到达过程,可用泊松分布拟合,方差和对应pixel强度的均值成比例(合理,强度越高来得越多,或者反过来说才对),在全图幅中非静止(not stationary,理解为不均匀)
- sensor chip中的热噪声/量化(discretization)导致的噪声
- 喷现有的方法不考虑噪声方差依赖于像素强度的特性,而关注人造、静止的噪声(i.i.d. Gaussian)
- 一些工作用heteroscedastic Gaussian分布建模intensity-dependent的噪声,这里Gaussian的方差是intensity-dependent,因为总噪声里的泊松成分可以由高斯近似所以合理。
- 还有的方法作variance stabilizing transform再进行stationary Gaussian denoise,不过这种变换会使得噪声分布非高斯。
- clean image acquisition的尝试以及2点不足:
- temporal averaging several noisy observations,忽略了由于clipping导致的噪声过程均值非0的特性
- 没有考虑后续raw转sRGB的非线性变换过程
- 当时仅有的真实噪声dataset RENOIR对纯净图片处理的pipeline不太合理:
- 图片对间有spatial misalignment
- 强度变换没有建模heteroscedastic noise
- low-frequency bias没有去除
- 基于8 bit demosaiced images,而DND基于untainted linear raw intensities
- 需要在不同ISO水平测定sensor的噪声特性
3. Image Model and Data Acquisition
3.1 Image formation
似曾相识(FFDNet还是RIDNet)的噪声模型:
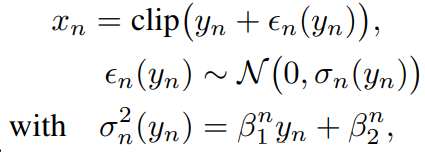
x_n是拍出来的含噪图片,\epsilon_n是近似为heteroscedastic Gaussian分布的噪声,clip是account for the saturation of pixels on the sensor(给我的感觉不是clip成整数,而是不超出maximum?这可能和raw数据的实际取值有关)。\sigma_n(y_n)称为noise level function。\beta主要取决于camera sensor和ISO值。由于clip,简单地noise level function平均噪声观测会产生误差,即\(\mathbb{E}[x_n \mid y_n]\neq y_n\),似乎可以根据y_n和\sigma_n(y_n)来表示\(\mathbb{E}[x_n \mid y_n]\)(给了个参考文献),将这种表示记为:
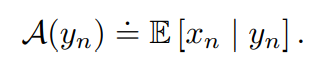
由于gt y_n不存在,所以用低ISO长曝光时间(保证两者乘积与x_n一致)的x_r作为gt。
4. Post-Processing
用来缩小y_r和y_n之间的差距。
定义了残差图片,比如R(x_r)感觉就是x_r的均值和x_n的差:
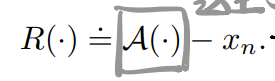
R(x_r)不是0均值的,这是因为:
- objects may move -> masking objects with a simple GUI tool
- spatial sub-pixel misalignments may be caused by small camera vibrations, e.g., due to the mechanical shutter -> model sa global 2D translation
- lighting of the scene may change slightly during capture, outdoors for example because of moving clouds, indoors for example due to light flicker -> final filtering step
- linear intensity changes arise from the fact that neither the analog gain nor the exposure time can be perfectly controlled -> model as linear scaling of pixel intensities
下面的具体细节目前不理解,也不打算去深入了解:
4.1 Linear intensity changes
4.2 Spatial misalignment
4.3 Low-frequency residual correction
5 Experimental Validation
好难,现在应该不需要理解…第一部分证明Post-processing有用,第二部分证明ground truth质量不错,第三部分讲noise parameters(\beta)的校正。
6. Benchmark
在三个set下做测试,分别是raw track、raw + VST track、sRGB track,有意思的结论:
- (当时的)判别式方法不太行,它们的泛化性不行(不能从训练分布泛化到实际噪声情形)
- 在sRGB域做去噪不如在raw域去噪效果好,因为sRGB域的噪声分布spatio-chromatically correlated
- 实际噪声能量水平显著低于学术设定