Brief review of image denoising techniques
2021/9/3
来源:一个线上期刊,感觉不是很好 - Visual Computing for Industry, Biomedicine, and Art 19
resource:github上备份的包括ipad标注的pdf版本。
作者是山大的Linwei Fan。
Summary:水平比较差的一篇综述,前面的传统方法总结得甚至不如印度人细,后面的NN-based方法实在太烂。
rating:0.9/5.0
comprehension:3.0/5.0(传统方法不太理解,不知道水平几何)
Introduction
- 噪声、边缘和纹理都是高频成分,在去噪的时候很难区分这三者,因此会不可避免地损失细节。
- 从数学的角度而言去噪是个inverse / ill-posed problem,没有唯一解。
- 去噪问题的定义还挺清楚的:
The purpose of noise reduction is to decrease the noise in natural images while minimizing the loss of original features and improving the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). - 去噪问题的挑战主要有:
- 平坦区域(flat areas)应该平滑;
- 边缘(edges)不能被模糊;
- 纹理(texture)应该被保护;
- 不能引入新的伪影(artifacts)。
Denoising Methods
甚至没能跳出这张图总结的范围(甚至不如三哥的总结):
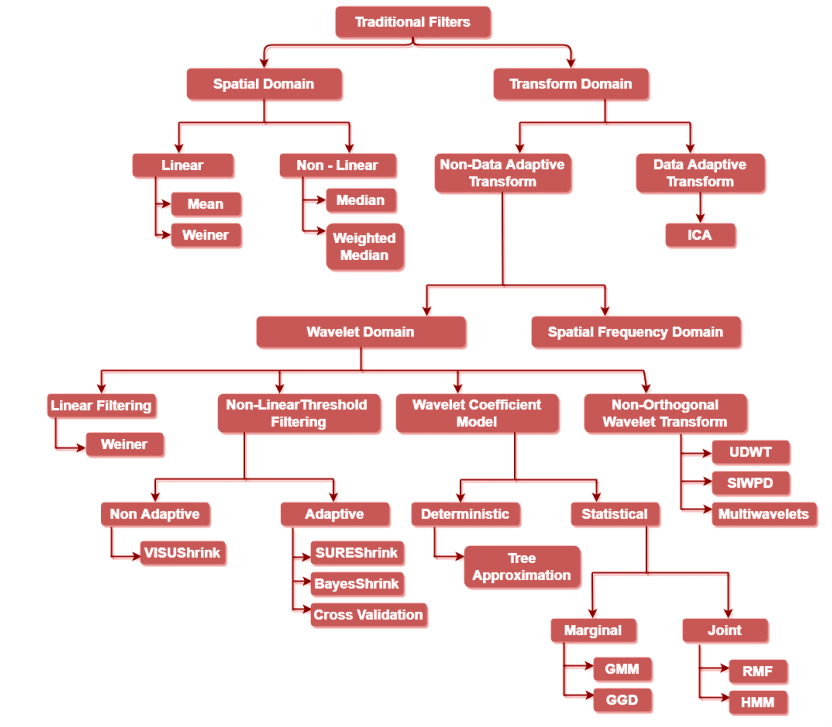
传统方法的分类为:
- Spatial Domain Methods
其定义为Spatial domain methods aim to remove noise by calculating the gray value of each pixel based on the correlation between pixels/image patches in the original image,也就是用像素/图像块之间的空间依赖关系计算合适的像素值进行去噪。- Spatial domain filtering
空间滤波器方法建立在噪声占据了频谱中的高频部分,使用低通滤波器可以去除噪声的理论基础上。- Linear Filters:可以在空间域去除噪声,但是很难保存纹理。e.g. Mean Filtering, Wiener Filtering.
- Non-linear Filters:e.g. Median Filtering, Weighted Median Filtering, Bilateral Filtering.
- Variational denoising methods(这块还挺难的)
变分去噪方法使用图像先验,通过最小化能量函数E来计算去噪后的图像,其动机是MAP:
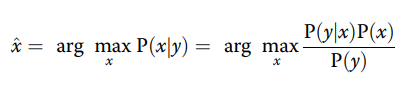
可以被等效地表示为:
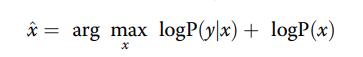
在AWGN的情形下,目标函数可以表示为:
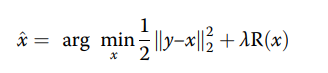
第一项表示原始图像和噪声图像之间的差距,被称为data fidelity项;第二项是正则项,变分去噪问题的关键就是找到合适的图像先验(第二项)- Total variation regularization
基于统计特性 - 自然图像局部光滑,像素值在大多数区域逐渐变化。可以保留sharp edge但是有三个缺点:1)over-smoothed texture, 2)flat areas are approximated by a piecewise constant surface resulting in a stair-casing effect, 3)losses of contrast - Non-local regularization
局部去噪时间复杂度低但是噪声等级高了之后效果就差,这是因为高等级的噪声会干扰临近像素之间的关系。e.g. NLM(non-local means), NSS(non-local self-similarity),WNNM(weighted nuclear norm minimization) - Sparse representation
每个图像patch都可以表示为over-complete dictionary中patch的线性组合。去噪的过程就是重建这个过程?可以灵活反应图像结构,缺点是忽略了图像的非局部关联。e.g. K-singular value decomposition (K-SVD) algorithm, NCSR(non-local centralized sparse representation, NSS+sparsity) - Low-rank minimization
将相似的patch建模为matrix,Each column of this matrix is a stretched patch vector. By exploiting the low-rank prior of the matrix, this model can effectively reduce the noise in an image,可以进一步分成- low rank matrix factorization 低秩矩阵分解就用两个小矩阵的乘积近似大矩阵。相似的patch被低秩分解以去除噪声。这类方法的缺点是必须将秩作为输入,太小的秩会损失细节,太高会保留噪声。
- NNM(nuclear norm minimization)
methods based on NNM aim to find the lowest rank approximation X of an observed matrix Y,NNM中参数的singular value都一样,改进的方法是WNNM(和上面有关系?又是A+B?)这类方法的缺点是计算开销大。
- Total variation regularization
- Spatial domain filtering
- Transform Domain Methods
变换域方法基于这样的观察:图像信息和噪声在变换域中的表现不同。根据变换基选择的不同,可以进一分成:- Transform domain filtering methods
- Data adaptive transform
e.g. ICA(Independent component analysis,适合去噪非高斯噪声), PCA
共同的缺点是计算代价高,因为需要采样没有噪声的数据because they use sliding windows and require a sample of noise-free data or at least two image frames from the same scene - Non-data adaptive transform
- spatial-frequency domain
像Fourier transform这样的,这种方法耗时较多,且取决于截断频率和filter的表现。 - wavelet domain
具有多尺度和稀疏性的特点。非常依赖小波基的选取,选取不当去噪效果就很差,所以是不具数据适应性的方法。- Linear
- Non-linear
- spatial-frequency domain
- Data adaptive transform
- BM3D
在变换域进行两次非局部协同滤波的方法。步骤是:- 相似的patch通过block matching堆叠成3D group;
- 3D group转换到小波域;
- 进行hard thresholding或者Wiener filtering;
- 根据系数进行逆变换(inverse transform)。
但是噪声等级逐渐增加BM3D的性能会下降很厉害,并引入伪影,尤其是在平坦区域。
- Transform domain filtering methods
Metrics of denoising performance & Conclusion
- 目前没有明确的数学方法来评价感官质量,感官质量主要取决于三方面:
- significant degree of artifacts
- protection of edges
- reservation of textures
- 结论里强调现在绝大多数的方法都致力于去除AWGN噪声,只有很少一部分考虑真实图像去噪(因为真实图像太难而且缺乏训练的成对图像)。