A High-Quality Denoising Dataset for Smartphone Cameras
2021/9/16
来源:CVPR18
resource:github上备份的包括ipad标注的pdf版本。
作者是York University和Microsoft Research的Abdelrahman Abdelhamed, Stephen Lin和Michael S. Brown。
Summary:raw image经典数据集SIDD,提供了10个场景下5种智能手机在不同的设置下拍出的约30000张噪声图像,以及对应的真实图像。同时设计了类似DND的真实图像后处理pipeline,着重解决由于(智能手机特有或者更为严重的)镜头移动(光学防抖)和径向畸变引起的misalignment、低光和过曝引起的clipped intensity问题。可以用下面的图进行总结:
Key words:
- 噪声原理
- 真实图像(raw)去噪benchmark
Rating: 4.0/5.0 珠玉在前,额外收获不多了。
Comprehension: 3.0/5.0 还是有些前情提要需要补充的,不过涉及具体方法我也不是很关心。
Abstract
- 由于小光圈和sensor size,智能手机图像中的噪声显著多于DSLR
- 本文出发点:当时没有基于智能手机镜头的dataset
- 用本文提供的real image - noisy image pair训出来的网络比用低ISO作为gt的数据集训出来的网络性能要好
1. Introduction
- 在smartphone上用低ISO图像当ground truth的策略行不通,因为低ISO图像中的噪声就很多
2.Related Work
- Ground truth for noisy real images 通常有两种思路:
- image averaging
- 基本方法是用静止的相机在静止场景中以相同的相机设置拍摄一系列照片,然后直接平均这些照片
- 但是这个方法的问题有:
- 当照片中有misalignment的时候会产生blurry mean image
- 由于低光条件或者过曝出现clipped value时噪声呈现出非0均值的情况,直接平均会有biasd情况
- synthetically generate noise
- 要求参考图片没有噪声,而且依赖噪声模型的准确性
- image averaging
- Denoising benchmark with real images
现有的数据集有:- RENOIR - pairs of low/high-ISO images
- lacks accurate spatial alignment
- low-ISO images still contain noticeable noise
- linearly mapped to 8-bit depth
- DND - pairs of low/high-ISO images
- 噪声水平低,缺乏低光环境的pair
- 使用global translation解决misalignment的问题,无法处理smartphone的特殊情形(lens motion/optical image stabilization, radial distortion)
- RENOIR - pairs of low/high-ISO images
3. Dataset
3.1. Image Capture Setup and Protocol
一些细节设置,不care:
- 室内场景,避免场景移动产生的misalignment
- 使用DC光源避免AC光源的flickering effect,光源可调亮度与色温
- five smartphone cameras (Apple iPhone 7, Google Pixel, Samsung Galaxy S6 Edge, Motorola Nexus 6, and LG G4)
- 更具体的设置参考3.1第二段以后,每个场景每个setting拍一连串照片
3.2. Noise Estimation
使用了两种噪声估计的方法:
- signal-dependent noise level function (NLF) - heteroscedastic signal-dependent Gaussian
- 所谓signal-dependent就是说总噪声中的泊松成分的方差和pixel intensity均值成比例
- NLF parameters provided by the camera device through the Android Camera2 API
- homoscedastic Gaussian distribution
- 为了照顾一般的去噪方法
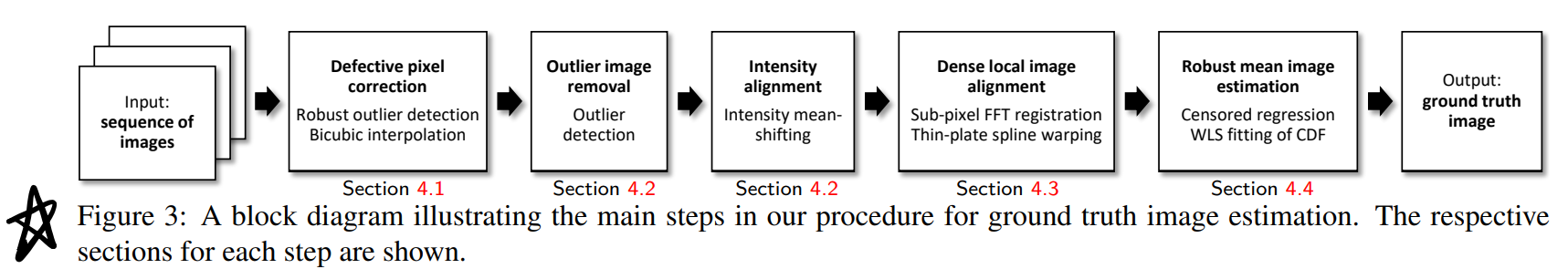
4. Ground Truth Estimation
包括下面几步:
- 去除坏点(Defective Pixel Correction)
- 两类坏点(来源没说,感觉可能是sensor的特性,每个sensor各异)
- hot pixels - produce higher signal readings
- stuck pixels - produce fully saturated signal readings
- 纯黑环境下拍500张照片,求均值图像,估计均值图像中pixel的高斯分布,再挑出来outlier当做defective pixel,对坏点作bicubic插值
- 具体方法不care
- 两类坏点(来源没说,感觉可能是sensor的特性,每个sensor各异)
- 对齐intensity
- 来源是硬件不精(slight changes in scene illumination and camera exposure time)
- 逐图像计算sequence里面每张图像的mean intensity,求这个mean的分布再剃掉outlier image
- Dense Local Spatial Alignment
- 为了去除shift in image content over the image sequence,其来源是combination of lens coaxial shift and radial distortion,根本原因是smartphone的optical image stabilization (OIS)
- 技术细节(建议略过):
- 做哪张图的ground truth就以哪张图作为ref,将sequence里面所有图切成有重叠的patch,patch越大越准;patch中点作为destination landmarks;
- 对每个图像中每个patch作关于参考图对应patch的accurate Fourier transform-based method to estimate the local translation vector,得到每张图的source landmarks
- 2D thin-plate spline image warping
- Robust Mean Image Estimation
- 根据sequence中的像素逐点算像素值。
- 细节:
- 先去掉possibly censored observations(取0和1的像素值,它们有偏,分别因为under-illuminated or over-exposed)
- 根据实际像素值计算empirical cumulative distribution function
- 根据噪声分布求parametric CDF(噪声数据哪来的)
- 用上面两个分布的加权平方误差和构造目标函数,优化这个式子估计像素的均值和方差
5. Benchmark
没太大用。
- 用他们数据集训出来的CNN更好使
- the mean PSNRs of benchmark images in raw-RGB and sRGB are 36.70 dB and 19.71 dB, respectively - 这个mean是哪来的?不是各种方法的平均和啊
- DND的噪声水平比SIDD低