FFDNet: Toward a Fast and Flexible Solution for CNN based Image Denoising
2021/9/9
来源:TIP18
resource:github上备份的包括ipad标注的pdf版本。
作者是HIT的Kai Zhang, Wangmeng Zuo, Lei Zhang等人,这哥们是真强啊,博士憋了两篇大的,现在在ETH Zurich当博后,羡慕了。
Summary:又是一篇很经典的deep denoising,特点是"fast, effective, flexible discriminative denoising"(感觉他们喜欢结合传统方法讲DL方法的去噪,有点历史底蕴)。主要特点是额外输入noise level map作为额外信息(对每个像素点有个噪声水平的flag,通过变化map也可以做到spatially variant denoise)和降采样在sub-image空间去噪以加速。能做到当noise map match噪声等级的时候达到sota、不知道噪声等级的时候控制去噪和保留细节的trade-off。
Key words: 降采样后去噪、额外信息(noise map)
Rating: 4.3/5.0
Comprehension: 4.5/5.0
一张图总结模型结构:
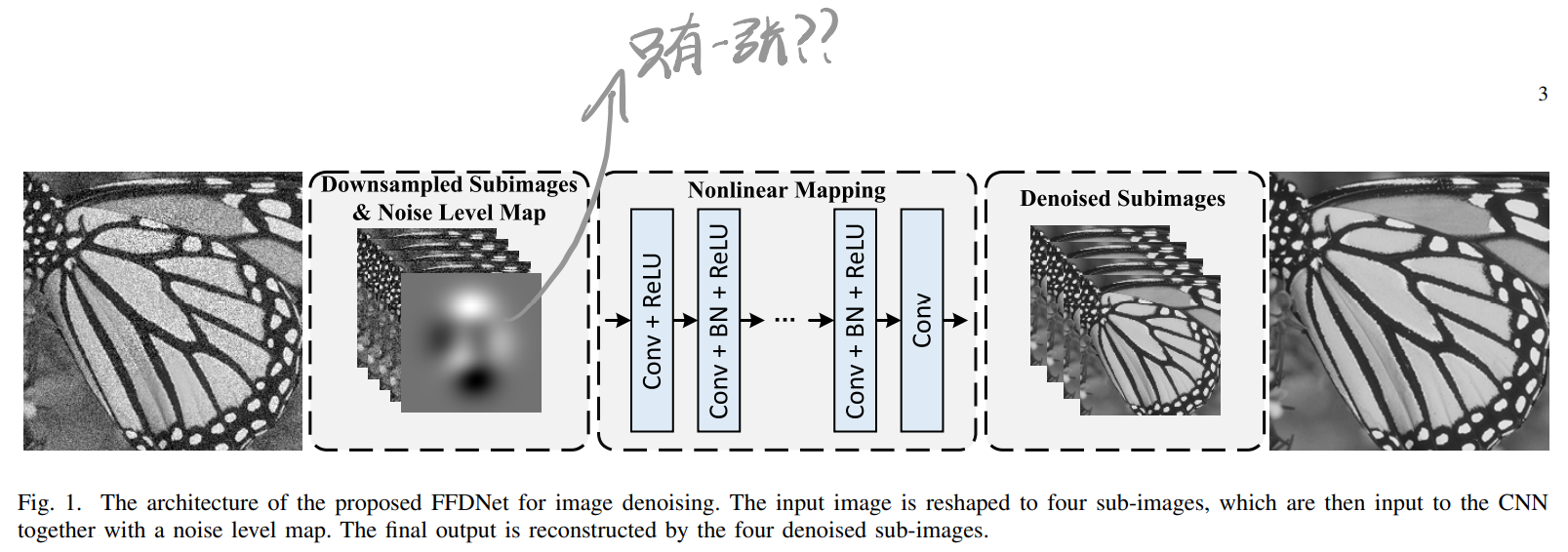
1 Introduction
- 现在看起来这些对去噪器的要求简直是萝卜坑:
- 使用一个model去噪;
- 快捷有效、用户友好;
- 噪声等级已知或者可以有效估计的时候能有效去噪、不知道或难估计的时候要平衡噪声去除和细节保留;
- 可以处理spatially variant noise。
- 图像去噪方法可以分成两大类:
- model-based methods
- time-consuming
- cannot be directly used to remove spatially variant noise
- employ hand-crafted image priors
- discriminative learning based methods
- learn the underlying image prior
- fast inference
- 具体可为learn stage-wise image priors in the context of truncated inference procedure与plain discriminative learning两类,第一类看不懂,有个简单的survey
- model-based methods
- 真实噪声的特点:
- signal-dependent
- non-Gaussian
- spatially variant
- 真实噪声的来源:
- camera imaging pipeline (e.g., shot noise, amplifier noise and quantization noise)
- scanning
- lossy compression and image resizing
2 Related Work
2.A MAP Inference Guided Discriminative Learning
看不懂,但我大受震撼。survey的时候或许能用到。
This method aims to learn the prior parameters along with a compact unrolled inference through minimizing a loss function.the methods only learn the prior parameters in a discriminative manner, while the inference parameters are stage-invariant.- 后面的方法也会学inference的参数:
learn stage-wise inference parameters - MAP inference guided discriminative learning:
- fewer inference steps
- very efficient
- (yet)
the learned priors and inference procedure are limited by the form of MAP model
2.B Plain Discriminative Learning
- learn a direct mapping function to model image prior implicitly
- better performance
- (yet) have to learn multiple models for handling images with different noise levels
- incapable to deal with spatially variant noise
3 Proposed Fast and Flexible Discriminative CNN Denoiser
3.A Network Architecture
- 第一层是个reversible downsampling operator(没说是bicbiuc还是strided downsample),而且noise map不逐通道,经过降采样之后特征图的尺寸是\(\frac{W}{2} \times \frac{H}{2} \times (4C+1)\)。因为用了downsample所以不需要用空洞卷积扩大感受野。
- 空间不变AWGN就是一张均匀的M。
- Conv部分第一层不加BN,最后一层只有Conv。
- FFDNet不预测噪声,直接输出原图。
- 彩色图像对应的通道数更多,原因倒挺能扯的:
- R,G,B通道间依赖关系很强,通道数多了可以鼓励探索通道间依赖关系;
- 彩色图像本身通道数就多。
3.B Noise Level Map
-
model-based denoising methods的优化目标是:
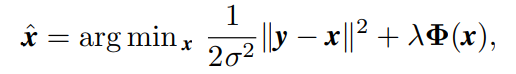
- 第一项是fidelity term(与噪声等级有关),第二项是regularization term(与图形先验有关)
- \lambda在噪声去除和特征保留间进行trade-off,太小噪声就会保留,太大就损失细节。
-
经过一定优化,上式可以改写成:
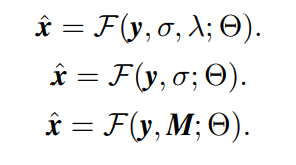
- \lambda可以被吸收进\sigma,上式第一行变成第二行;改写之后可以通过\lambda平衡噪声去除与细节保留(因此model-based methods可以通过改变\sigma灵活去噪)。
- 虽然y和\sigma尺寸不一样,align之后就成了第三行,也就是对每个pixel指定一个noise level
- M可以进一步拓展成spatially variant或者channel variant
3.C Denoising on Sub-images
- 提升efficiency的两条路径:
- 减通道数 -> 损害model capacity
- 改dilated Conv -> 在尖锐边缘处产生效应
- 没说具体的降采样方法,我可以理解为desubpixel吗?毕竟用了"可逆"字眼,而且最后是通过subpixel逆转。
3.D Examining the Role of Noise Level Map
- 当M和真实噪声水平不匹配的时候训练会出现问题,M不再能平衡去噪与细节保留。
- 解决方法之一是对Conv kernel正则 - orthogonal regularization,可以:
- eliminating the correlation between convolution filters
- facilitating gradient propagation
- improving the compactness of the learned model
- enhancing the network generalization ability
- 真的吗?我不信。
- 或者嗯训直到训出来能妥善解决问题的model
- 解决方法之一是对Conv kernel正则 - orthogonal regularization,可以:
3.E FFDNet vs. a Single Blind Model
这里居然喷起来盲去噪了,这不是欺负人?你把你noise map给我下了
- blind与non-blind的区别:
- generalization ability:blind的更差(难以接受),难以泛化到真实噪声
- the performance for AWGN removal:blind的更差(难以接受),没有noise map不是直接去世?
- application range:blind的更窄(难以接受),
non-blind model can be easily plugged into variable splitting algorithms to solve various image restoration tasks
3.F Residual vs. Non-residual Learning of Plain CNN
- 承认了residual learning会受益于Gaussian情形
- 有BN的时候,无论用不用残差学习,调优之后性能都一样。
- 深度合适的时候就不用Residual了,好笑。
3.G Un-clipping vs. Clipping of Noisy Images for Training
- 结论:虽然加完噪声clip到[0, 255]的范围符合图像像素值的分布,但是没必要(因为会破坏高斯分布),不如不clip。
- clip会使得噪声偏移真实AWGN
- variable splitting algorithms中有一类子问题从贝叶斯角度相当于高斯去噪问题,扩大了高斯去噪问题的范围
- 噪声等级高了之后clip会破坏0均值特性
4 Experiments
- 使用的数据集有
- BSD68
- Set12
- RNI6/RNI15
- tailored ImageNet
- Waterloo
- CBSD68
- Kodak24
- McMaster
- 测试关心的点:
- AWGN Removal(color/greyscale)
- Spatially Variant AWGN Removal(特色)
- 对M进行了bilinearly采样,由于M本来就经过了空间平滑,使用降采样map对结果影响也不大。
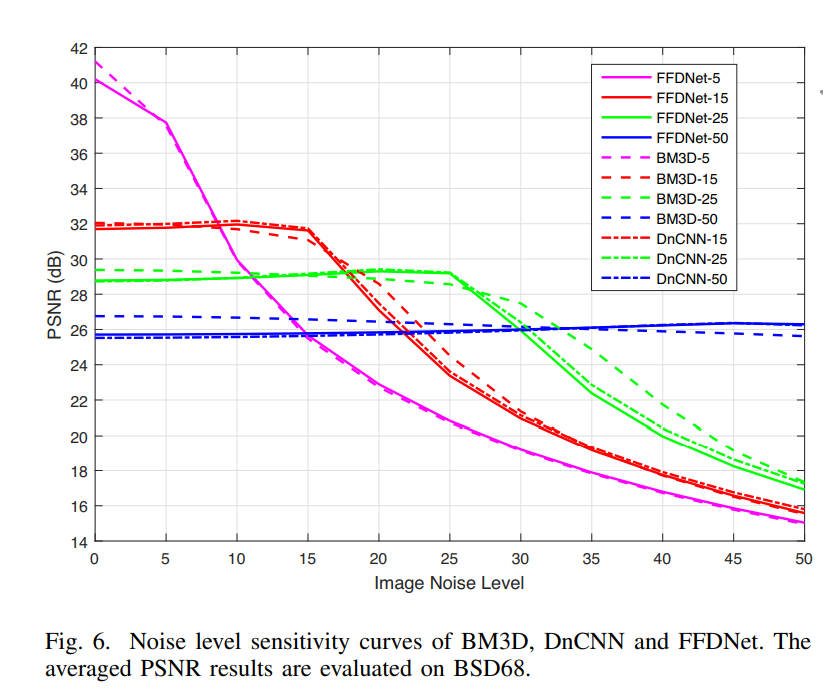
- Noise Level Sensitivity
- 这节评估mismatch的容忍度。
- 有一张图可以记下,当GT噪声强度低于指定噪声水平时PSNR几乎不变,GT噪声水平升高PSNR逐渐降低:
- Real Noisy Images(generalization)
- 使用手工绘制M的方式调节噪声等级,首先全图grid搜索找个baseline出来,再patch-wise fine-tune,根据patch插值全图
- Running Time
- 这次又计算CPU-GPU搬运时间了