Noise2Noise: Learning Image Restoration without Clean Data
2021/9/24
来源:ICML18
resource:github上备份的包括ipad标注的pdf版本。
作者是NVIDIA的Jaakko Lehtinen, Jacob Munkberg, Jon Hasselgren, Samuli Laine, Tero Karras, Miika Aittala, Timo Aila等人,Jaakko Lehtinen好像是个大佬,羡慕。
Summary:一篇非常棒的论文!第一次读论文这么开心!全文的核心思想非常简单,就是用含有噪声的target训练模型,而不需要获得纯净图像(也就是不需要显式的图像先验或者退化过程的似然模型)。做了很多的应用,比如加性白高斯噪声的去除、去文字、MC渲染、MRI去噪,总之感觉非常有趣!!
Key words:
- Noisy Targets
Rating: 4.5/5.0 非常不错!开了denoise领域self-supervision的路!(原理)简单但是作用很大受众很广!我非常喜欢!第一次读论文这么开心!
Comprehension: 2.5/5.0 我看不懂,但我大受震撼。
2. Theoretical Background
以SR任务为例,一个低分辨率图x可以对应许多不同的高分辨率图y,这是因为关于边缘和纹理的精确位置和方向的信息在抽取中丢失,换句话说,\(p(y \mid x)\)是与低分辨率图x一致的高度复杂的自然图像的分布(p(y \mid x) is the highly complex distribution of natural images consistent with the low-resolution x)。当使用L2 loss,通过成对的图像对训练网络时,网络会试图去输出各种解释的平均,这样会最终导致模糊的输出,但是这种输出也可以反过来加以利用。
A trivial, and, at first sight, useless, property of L2 minimization is that on expectation, the estimate
remains unchanged if we replace the targets with random numbers whose expectations match the targets
对于公式(5):
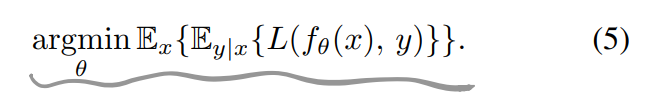
如果input-conditioned目标分布\(p(y \mid x)\)被替换成了有same conditional expected values的目标分布,网络中的最优参数\theta不会发生改变。(The optimal network parameters \theta of Equation (5) also remain unchanged, if input-conditioned target distributions p(y|x) are replaced with arbitrary distributions that have the same conditional expected values),这意味着原则上使用零均值的噪声污染target不会影响网络学到什么,即有:
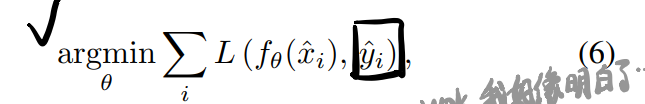
这里输入和目标都是从受到污染的分布中采出来的(而这个分布不一定一样,但只要满足\(\mathbb{E}\{\hat{y_i} \mid \hat{x_i} \} = y_i\)即可)。对于无限的数据,这个解和公式(1),即下式一样:
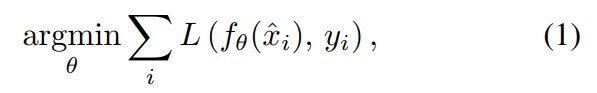
而对于有限的数据,方差是目标targets中corruptions的平均方差除以训练sample的数量,但是这些和corruption的似然模型或者潜在纯净图片的密度模型(prior)都没有关系。因此,我们不需要显式的p(noisy \mid clean)或者p(clean),只需要我们有根据它们分布的数据。
3. Practical Experiments
3.1. Additive Gaussian Noise
零均值加性高斯白噪声,对应L2 Loss。
- Convergence speed:训练时training loss不会下降,training loss一直很大。但是虽然ACT的梯度很noisy,weight的梯度相对很纯净。根据figure1 loss收敛速度和纯净的很接近,而且性能也很接近。
- 提到了一种Brown Gaussian noise,是pixel-wise引入相互关联的噪声,具体做法是使用一种不同带宽的Guassian filter模糊白噪声并维持噪声水平为25
- Finite data and capture budget:结论是budget一致时noisy target效果更好。
3.2. Other Synthetic Noises
- Poisson noise:dominant source of noise in photographs; zero-mean; harder to remove because it is signal-dependent; L2 loss
- 有一段奇怪的描述,大意没搞错应该是说dark current and quantization导致的噪声可以被转换成0均值的类型,所以也可以套?
- Multiplicative Bernoulli noise(New Type!):constructs a random mask m that is 1 for valid pixels and 0 for zeroed/missing pixels; 没说有什么特性,认为是L2吧
- Text removal(New Type!):The corruption consists of a large, varying number of random strings in random places, also on top of each other, and furthermore so that the font size and color are randomized as well. The font and string orientation remain fixed; median is the correct statistic -> L1 Loss
- Random-valued impulse noise(New Type!):以概率p将pixel替换成均匀采样的值,以1-p的概率保持原样,与椒盐噪声(将pixel替换成黑/白)不同,这里是替换成随机色彩。the desired output is the mode of the distribution -> "L0 Loss"
3.3. Monte Carlo Rendering
蒙特卡洛渲染!!有意思!!!还有HDR!!!计算机图形学真有趣!!!
- Denoising Monte Carlo rendered images:用64 samples(path)/pixel的pair去训练网络,代替131k sample/pixel的ground truth,能快上2000倍!太酷了!!!
- Online training:足够快
3.4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI:Modern MRI techniques have long relied on compressed sensing (CS) to cheat the Nyquist-Shannon limit: they undersample k-space, and perform non-linear reconstruction that removes aliasing by exploiting the sparsity of the image in a suitable transform domain.
俄罗斯轮盘采样10%频谱,对着训练。